Introduction
In a move that could significantly impact Android power users, Google has updated its Play Integrity API to enforce stricter hardware-backed security measures Google Play Integrity API. The update affects users with rooted devices, unlocked bootloaders, and custom ROMs—who may now be blocked from accessing banking, gaming, and other sensitive applications.
What Is the Google Play Integrity API?
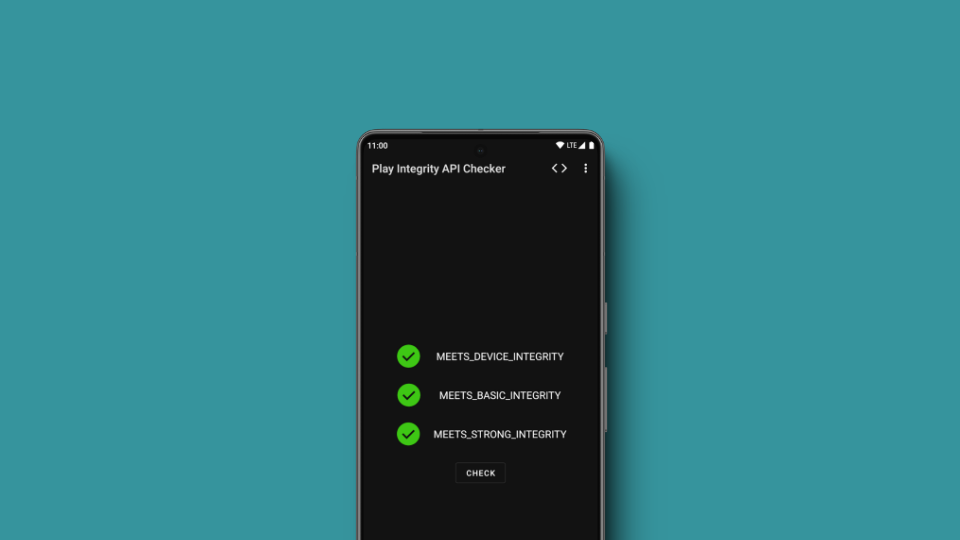
The Play Integrity API is a security tool that helps app developers ensure their applications run on trusted, unmodified Android devices. It delivers three types of verdicts:
- Basic: Minimal integrity check
- Device: Confirms OS and device are recognized and certified
- Strong: Uses hardware-backed checks to ensure uncompromised software and recent security patches
What Changed in 2025?

As reported by Android Authority, the API’s “device” verdict now relies on hardware-backed signals, making it far more difficult to spoof or bypass. Google announced this update back in December 2024, and it is now rolling out to all apps requesting device-level integrity.
Key Impact Points:
- Rooted phones and custom ROMs will fail Play Integrity checks.
- Apps requiring device integrity (like banking, streaming, and finance apps) may become inaccessible.
- Phones without a security update in the past 12 months may also be restricted.
Why Rooted Phones and Custom ROMs Are Affected
Custom ROMs and root access typically involve unlocking the bootloader, which compromises Android’s secure boot and trusted execution environment. With hardware-backed verification in place, the API can now detect these modifications with far more precision.
Security vs Freedom: A Tough Choice for Power Users
This update forces a dilemma for Android enthusiasts: continue running mods and custom firmware—or revert to stock Android to maintain app compatibility. Google’s tightening of the Play Integrity framework reflects its broader push for stronger security across the Android ecosystem.
Older Devices Without Security Patches Also at Risk
The new “strong” verdict includes a check for whether the device has received a security update within the last year. This means that even users with factory-stock Android devices may lose access to some apps if their OEM has stopped issuing updates.
Conclusion
Google’s updated Play Integrity API significantly raises the security baseline for Android app access. While this protects users from malicious interference, it also restricts freedom for those who enjoy customizing their devices. As Android 16 rolls out, users will need to decide what matters more: customization or compatibility.








