Introduction: A Silent Satellite Sends a Loud Signal
In one of the most puzzling space science events of 2024, astronomers detected a brief but powerful radio burst near Earth NASA Relay 2 satellite. Initially believed to originate from a cosmic source like a pulsar, the signal was eventually traced to something far more surprising — NASA’s defunct Relay 2 satellite, which has been silent since 1967. The finding sheds light on both the unpredictability of space debris and the hidden risks of aging satellites.

Relay 2: From Decommissioned to Mysterious
Relay 2, a NASA communications satellite launched in 1964, stopped functioning after just three years. Yet more than 60 years later, it may have emitted the brightest radio flash in the sky, according to a preprint study on arXiv posted June 13, 2025. The signal was detected by the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP), a powerful radio telescope array.
Signal Detection: Not from Deep Space
Most powerful radio bursts originate from outside our galaxy and are often attributed to high-energy phenomena such as magnetars or neutron stars NASA Relay 2 satellite. But this 30-nanosecond signal had an unusual signature. ASKAP scientists determined it came from Earth’s vicinity, too close for cosmic attribution. After a detailed orbital trajectory analysis, the source was aligned with Relay 2’s decayed orbit.
The ASKAP team considered—and then ruled out—typical cosmic sources, pointing instead to the satellite as the most likely origin.

What Could Have Caused the Burst?
Two primary explanations emerged for this anomalous signal:
- Electrostatic Discharge (ESD): Charge accumulation on Relay 2’s outdated surfaces may have triggered a discharge, similar to lightning.
- Micrometeorite Impact: A small particle striking the satellite could have generated a plasma cloud, releasing the detected signal.
Space physicists currently favor the ESD theory, citing how older spacecraft materials—lacking modern shielding—can build up static electricity and release it suddenly. These findings offer a rare opportunity to study aging satellites in situ.
Why This Matters: Understanding Satellite Decay
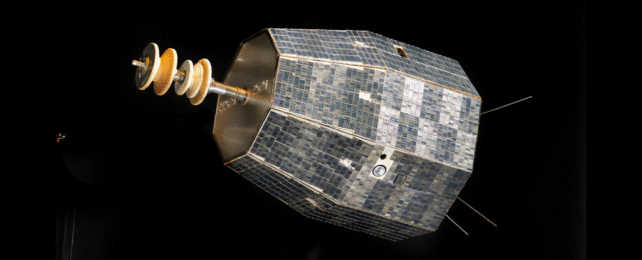
While dead satellites typically remain inert, this case highlights that they can unexpectedly emit radiation, creating challenges in both satellite health monitoring and space traffic management. As orbital congestion increases, researchers are calling for new tools to detect and catalog these accidental emissions.
Dr. Karen Aplin, an atmospheric physicist, told New Scientist that such signals could eventually serve as a novel way to monitor dead satellites and small debris. “This may open the door to a new branch of observational space physics,” she added.
Relay 2 and the Growing Threat of Space Debris
Relay 2 is just one of thousands of decommissioned satellites orbiting Earth. Events like this reinforce concerns about aging space objects and the dangers they may pose. Even inactive hardware may carry enough residual energy or unstable components to emit unexpected phenomena.
Conclusion: A Wake-Up Call from the Past
The detection of a 2024 radio burst from a 1960s NASA satellite proves that even dead hardware can “speak” from space. With further study, scientists may unlock new ways to monitor and manage space debris — not just to protect operational spacecraft but also to better understand how old technology behaves in extreme environments.
As the satellite economy grows and space gets increasingly crowded, this case study of Relay 2’s unexpected signal could serve as a crucial example for future missions and orbital safety strategies.
📌 Related Reading










