Vegan diets have gained immense popularity for their health and environmental benefits. However, one often-overlooked challenge is ensuring adequate intake of essential amino acids like lysine and leucine. These amino acids are crucial for muscle function, immune health, and overall well-being.
Understanding Protein Deficiency in Vegan Diets
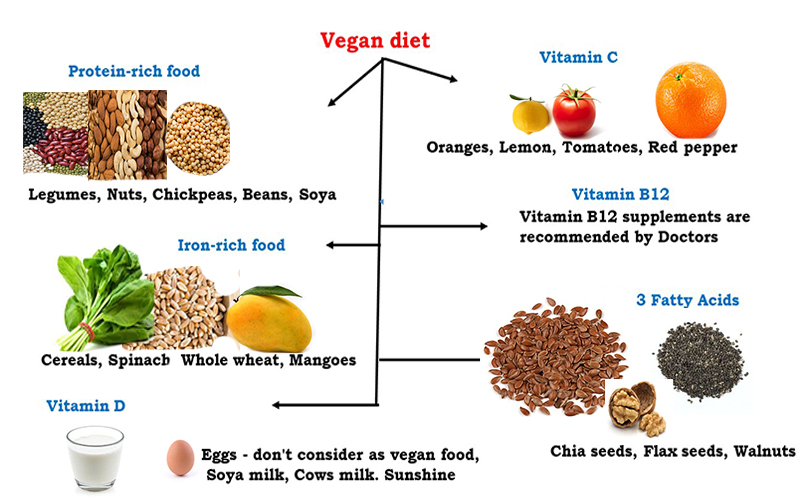
While most vegans get enough protein, it’s the quality and specific amino acid profile of their protein sources that often fall short. Research shows that while total protein intake may be sufficient, essential amino acids like lysine and leucine are commonly under-consumed in plant-based diets.
What Are Lysine and Leucine?
Lysine and leucine are vital amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own, making them essential through diet. Lysine is necessary for tissue repair, calcium absorption, and immune function, while leucine plays a key role in muscle building and recovery.
A new study from Massey University in New Zealand, published in PLOS ONE on April 16, 2025, examined the protein intake of individuals following long-term vegan diets. The researchers, led by Bi Xue Patricia Soh, found that while most participants consumed enough total protein daily, a significant number did not meet the recommended intake for two essential amino acids: lysine and leucine.
Proteins are composed of amino acids, which serve as fundamental building blocks for the body. Although the human body can produce many amino acids on its own, there are nine “indispensable amino acids” that must be obtained through diet. Because plant-based foods often contain lower or more variable levels of these essential amino acids compared to animal-based foods, meeting amino acid requirements can be more challenging for those on vegan diets.
Why Are Vegan Diets at Risk?
Many plant-based foods contain lower levels of these essential amino acids, making it harder to meet daily requirements. Legumes, seeds, and nuts can provide lysine and leucine, but they must be consumed in sufficient quantities to be effective.
Improving Lysine and Leucine Intake
- Legumes and pulses: These foods are rich in lysine, and when paired with other plant foods, they help improve overall protein quality.
- Tofu and tempeh: These soy-based products are excellent sources of protein and can help boost leucine intake.
- Quinoa: A complete plant protein that contains all nine essential amino acids, including lysine and leucine.
Conclusion: Ensuring a Balanced Vegan Diet
While a vegan diet can provide all the nutrients needed for good health, attention must be paid to achieving high-quality protein intake. By incorporating a variety of plant-based foods and understanding amino acid profiles, vegans can thrive without nutrient deficiencies. If you feel your diet may be lacking, consult a nutritionist for personalized advice.









